Editor's note: Every Monday for the next few weeks, we'll spend some time digging into the similarities between the U.S. economy from after World War II and today. Be sure to check back each week to keep up with our coverage of the timeline.
 'As prices go up, your savings go down'...
'As prices go up, your savings go down'...
The mainstream financial media has been repeating this same story for months.
It started in January, when ABC News and other outlets began reporting that rising inflation was depleting Americans' savings.
Then in June, Forbes talked about how Americans are being forced to make tough spending decisions because they're dipping into savings.
And just last week, the Wall Street Journal said the Fed's inflationary risk controls will send the economy into a tailspin.
These stories are certainly scary for consumers. They paint a picture of inflation as a monster that's putting holes in Americans' wallets.
It's true that rising prices put many of us on the back foot. But as with many things, the situation isn't necessarily as bad as the media makes it seem.
 If we look back to historical trends, we can begin to ease some of these fears...
If we look back to historical trends, we can begin to ease some of these fears...
Last week, we talked about the 1945 recession and its similarities to today's economy. Back then, the U.S. navigated a recession without skipping a beat. This was thanks to strong employment demand and underlying nominal gross domestic product ("GDP") growth as we emerged from war.
But it didn't end there. The economy continued to chug along after 1945, as well.
Soldiers who returned home began to focus on building their families. And those families began to invest in their homes. Most notably, people started dipping into their savings.
During the war, savings grew. Americans were either fighting overseas or they were rationing at home to support the war effort.
Now that the fighting had ended, folks were ready to spend. But this surge in spending – and demand – led to an issue... a lack of supply.
American factories had spent the previous few years focused on the war. They weren't ready for this shift in consumer trends. Customers no longer needed planes, tanks, and guns. Instead, they wanted fridges, ovens, and cars.
With so much demand and so little supply, inflation skyrocketed.
In May 1946, inflation was roughly 3%. By November, that number had risen to almost 18%. And it stayed at or above that level until July 1947, when it dropped to 12%.
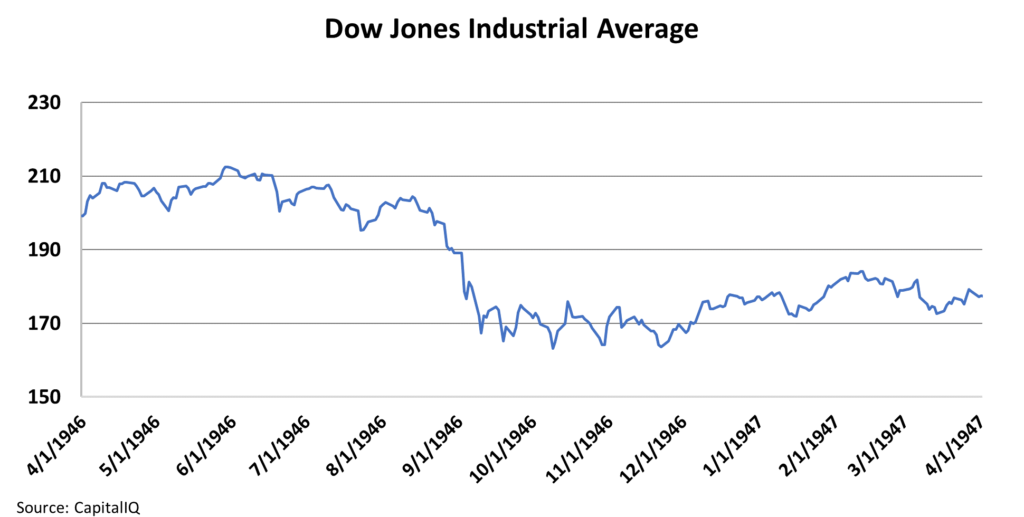
When this surge in inflation began to look like a problem, the market took notice. The Dow Jones Industrial Average peaked in June 1946 after the recession ended. Over the next 12 months, it declined 22%, from around 210 to 163.
 Sound familiar yet?
Sound familiar yet?
As investing pioneer John Templeton said, "The four most dangerous words in investing are: this time it's different."
That's why it's important to study the ways history lines up with the current market.
In 1945, inflation soared because of immense pent-up savings that flooded the economy when it wasn't ready. The market dropped because investors were concerned that an inflation spiral could lead to higher sustained prices... which could impact businesses, stocks, and interest rates.
But if late-1940s reporters had written articles about how inflation was eating away at consumer savings, they would have had the story backward. The same is true of today's journalists.
In reality, inflation isn't necessarily eating into savings. Rather, consumers are aggressively deploying the savings they had grown during the pandemic. And supply can't keep up with this surge in demand.
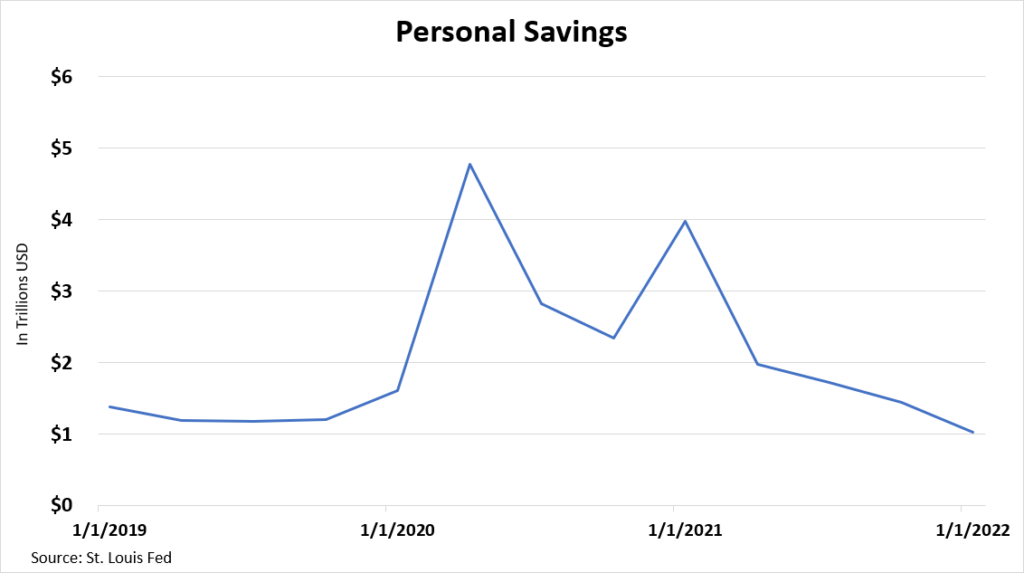
Total gross private savings and personal savings both jumped massively during the pandemic.
Personal savings were at $1.2 trillion in December 2019 – almost an all-time high. By April 2020, this figure climbed to nearly $4.8 trillion. That's a staggering 300% growth in savings in just four months.
Once COVID-19 vaccination rates ramped up, consumers stopped saving. Instead, they started spending again, both at home and on travel and experiences.
Backlogs for consumer goods built up. Demand was massive.
One of our analysts, Kyle, sold his years-old furniture for almost the cost he paid when it was new. That's just one example, of course... But it goes to show how much people were willing to pay to get what they wanted.
At the same time, travel started to pick up in fits and starts. People started to live their lives again, venturing out of their homes to restaurants and bars. They'd been cooped up for a year, growing their savings. Now, they were ready to get "revenge" using their bank accounts.
Last week, we mentioned that our emergence from the COVID-19 pandemic mirrored the end of World War II. The post-war inflationary trend matches the current economic conditions, too.
In both cases, consumers deployed their savings aggressively. In the past 15 months, savings levels have boomeranged. They're now in line with where they were in the post-Great Recession period. Total gross private savings are approaching first-quarter 2019 levels.
There's no surprise here – it's just like what happened in the post-war economy. A massive deployment of savings led to an epic inflation hike.
This time around, inflation didn't get as bad as it did back then (even though the markets tanked in similar fashion). But even so, what happened in 1946 can tell us a lot about what to expect from here.
Next week, we'll talk about what the Fed did next... how investors and the economy reacted... and most important, what the market's past can tell us about how to invest today. Be sure to check back in each week for the latest installment in this series.
Regards,
Joel Litman
July 18, 2022



 'As prices go up, your savings go down'...
'As prices go up, your savings go down'...